Latest picking start
The latest picking start (LPS) is the point in time at which the picking for the delivery must be started to arrive in time at the customer. If the latest possible picking start for a certain delivery date in a facility isn't known, it can be requested via the checkout options REST API endpoint. Our systems then calculate the latest picking start based on cutoff times of carriers and the fulfillment process buffer.
Latest picking start calculation
General
When processing checkout options REST API or orders that involve querying future availability, it is necessary to determine the appropriate point in time to request inventory data. As a result, it can be decided if enough stock will be available at the point in time when the order must be picked latest. This ensures that the order is delivered on the customer's desired date. Especially with stock that is perishable, it makes sense to maintain expiry dates to ensure goods are delivered to customers in optimal freshness.
The calculation for the LPS is performed when:
using the checkout options REST API endpoint when a "desired delivery time" is included and the reservation preference mode is set to "ALAP" (as late as possible)
performing a routing with an order where a "desired delivery time" is included and the reservation preference mode is set to "ALAP" (as late as possible)
The latest picking start is calculated per facility carrier connection and for potentially possible delivery days. This means that one facility could have multiple latest picking starts. Finally, the LPS with the most available requested stock is chosen.
The following information is required for LPS calculation:
The desiredDeliveryTime in the order or in the corresponding checkout options call
The reservation preference mode "ALAP" (as late as possible)
At least one active carrier
At least one active facility-carrier connection
A defined delivery time (with optionally, additional configuration settings)
If any required data is missing, the LPS cannot be calculated. In such cases, the system either assumes zero stock for subsequent processes (e.g., during order routing) or generates an error (e.g., when calling a checkout option endpoint).
Example
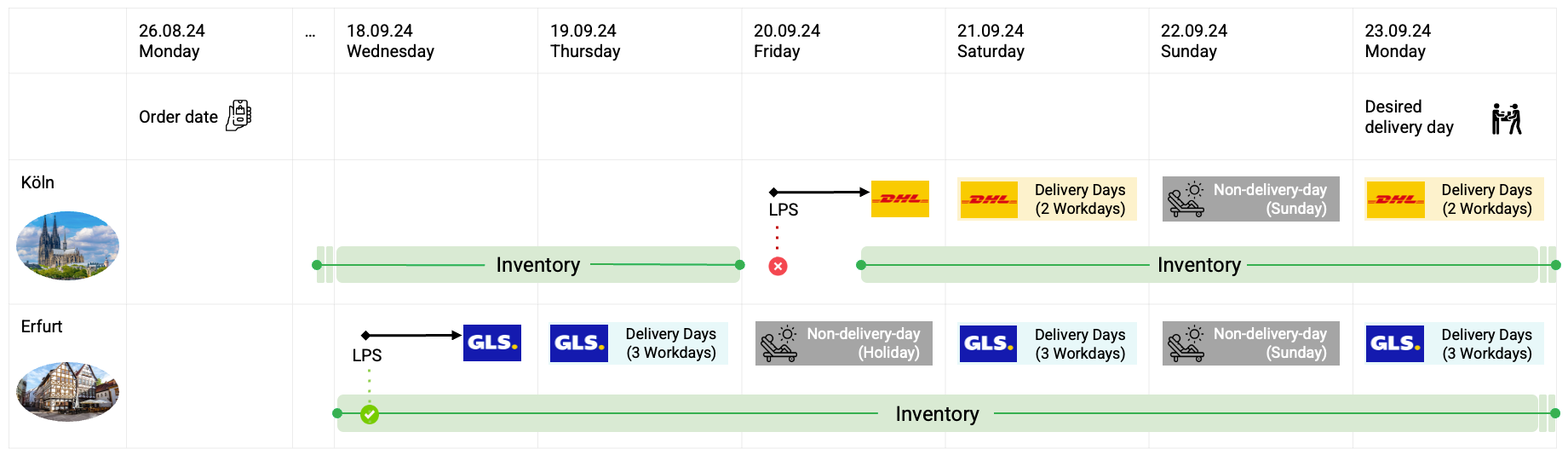
A typical use case is a customer placing an order which should be delivered at a specific day in the future (in the chart below the request is 26 August. requesting for a delivery on 23 September).
For calculating a LPS, the delivery times per carrier as well as non-delivery days are checked. Afterwards, the facility's fulfillment times, average fulfillment duration, and fulfillment capacities are examined to determine which cutoff time can be reached.
Last updated

