Event export
The system logs all fulfillmenttools events and makes them available in a daily export. The daily event files are saved in a Google Cloud Storage bucket, enabling users to leverage data from their fulfillment process for additional processing and analytics.
Event export functionality isn't activated by default. Use the contact form to ask us to enable it for you.
Accessing the bucket
Google offers multiple client libraries for accessing Google Cloud Storage buckets, and you can also use the Google Cloud Storage API directly. Another alternative is to use the gcloud CLI from the Google Cloud SDK.
Accessing the bucket requires a Google service account. Upon request, fulfillmenttools provides a service account key for authentication. This service account grants access only to this specific bucket. It can't be used to access the fulfillmenttools API or its client applications.
The service account key will be a file named {projectId}-{key_id}.json. This file contains a JSON representation of the service account.
This file contains the service account key and allows access to the bucket, so make sure to store it securely. See the official Google documentation for further information.
File and folder structure
The bucket is named {projectId}-{TIER}-public-events-export-bucket and is only accessible by authorized accounts.
For each day, the system creates a folder in the bucket with the pattern YYYY-MM-DD that contains the events for that day.
Each folder contains one or more gzipped files. Each of these files contains multiple lines, each corresponding to an event in fulfillmenttools.
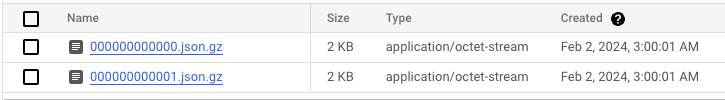
Each line of a file is a JSON object containing metadata fields (id, eventName, created) and the event payload.
Retention
The system stores data in the buckets for 90 days. After this period, the data is automatically deleted.
gcloud CLI example
The following example demonstrates how to copy files from a Google Cloud Storage bucket using the Google Cloud CLI.
Check the official Google documentation about gsutil for further details.
Activate the service account
The service account email ID is located in the client_email field of the provided key file. Use this ID to activate the service account:
The command gcloud auth list lists all credentialed accounts and shows the active one. The gcloud config list command can be used to check the current configuration.
List files in the bucket
The following commands list the contents of the bucket:
Download the whole bucket
Individual files or the entire bucket can be downloaded to a local folder:
Last updated

